

Here are some critical Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds problems for Class 10 Science. These inquiries are intended to aid students in studying for and performing well on the CBSE Class 10 Science Examination 2023–24. Students can clear up their concerns and be ready for the exams by practising different types of questions. By answering these questions, you'll increase your confidence while also sharpening your problem-solving abilities.
In Chapter 4 of Carbon and its Compounds you will learn about The Covalent Bond, Versatile Nature of Carbon,Chemical Properties of Carbon Compounds,Important Carbon Compounds-Ethanol and Ethanoic Acid,Soaps and Detergents.
Ans. (d)
Explanation:
Alkanes are known as saturated compounds. All the alkenes and alkynes with double and triple bonds in their carbon atoms are known as unsaturated alkenes. So propene and propyne are unsaturated compounds.
Ans. (c)
Explanation:
The successive members of a homologous series differ by a CH2 group. The molecular mass of a CH2 group is 14 amu. Hence, each successive homologue of a homologous series differs by a mass of 14 amu.
Explanation:
The molecular formula of two consecutive members of a homologous series differ by CH2.
Explanation:
Catenation and tetravalency are the two properties of carbon which leads to the formation of a large number of carbon compounds.
Explanation:
(i) Ethene is formed when ethanol at 443K is heated with excess concentrated sulphuric acid.
The mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene is:
1. First step is the protonation of the oxygen atom of the −OH group.
2. Second step is the loss of a molecule of water to form carbonium ions.
3. Last step is deprotonation to form a carbon- carbon double bond.
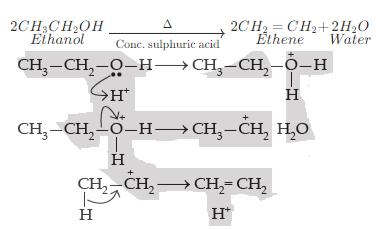
Concentrated sulphuric acid can act as a dehydrating agent. Hence, ethanol when heated at 433 K with excess conc. H2SO4 undergoes a dehydration reaction to form ethene.
(ii) Hydrogenation is the process of addition between hydrogen and other compounds in presence of a catalyst.
For example: Alkene can be converted to alkane by using H2 in presence of metal catalyst such as Pt, Ni or Pd
CH2 = CH2 → CH3CH3
The industrial applications are as follows:
1. To convert alkenes into alkanes.
2. To prepare vegetable ghee from vegetable oils.


oswal.io offers a thorough set of questions for learning the topic in a better way if you're looking to further practise and improve your grasp of the concepts covered in the chapter.
Ans: Covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points because the forces of attraction between molecules of covalent compounds are very weak. On applying a small amount of heat these molecular forces break.
Ans: (i) C2H4 belongs to alkene series having a general formula, CnH2n.Thus, next homologue will be C3H2×3 = C3H6
(ii) C4H6 belongs to the alkyne series having general formula, CnH2n-2.Thus, next homologue will be C5H2×5-2 = C5H8
Ans: Ionic compounds are formed either by gaining or losing electrons from the outermost shells, but carbon which has four electrons in its outermost shell cannot form ionic bonds because
1. If carbon forms ionic bonds by gaining four electrons to attain a noble gas configuration then it would be difficult for six protons in the nucleus to hold ten electrons.
2. If carbon forms ionic bonds by loss of four electrons then it would require a lot of energy to remove these electrons from the outermost shell.
Due to these reasons carbon forms covalent bonds by sharing the valence electrons.
Type of bonds formed in ionic compounds are called electrovalent bonds and the type of bonds formed in carbon compounds are called covalent bonds.
Ans: (i) As carbon has four valence electrons and it can neither lose nor gain our electrons thus, it attains noble gas configuration only by sharing of electrons. I bus, it forms covalent compounds.
(ii) In diamond, each carbon atom is bonded to four other carbon atoms forming a rigid three-dimensional structure. This makes diamond the hardest known substance. Thus, it has a high melting point.
(iii) In graphite, each carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms by covalent bonds in the same plane giving a hexagonal array. Thus, only three valence electrons are used for bond formation and hence, the fourth valence electron is free to move. As a result, graphite is a good conductor of electricity.
Ans: Covalent bonds are those bonds which are formed by sharing of the valence electrons between two atoms. Electron dot structure of methane is shown in the figure.

Covalent compounds are generally poor conductors ol electricity because they do not have tree electrons or ions.